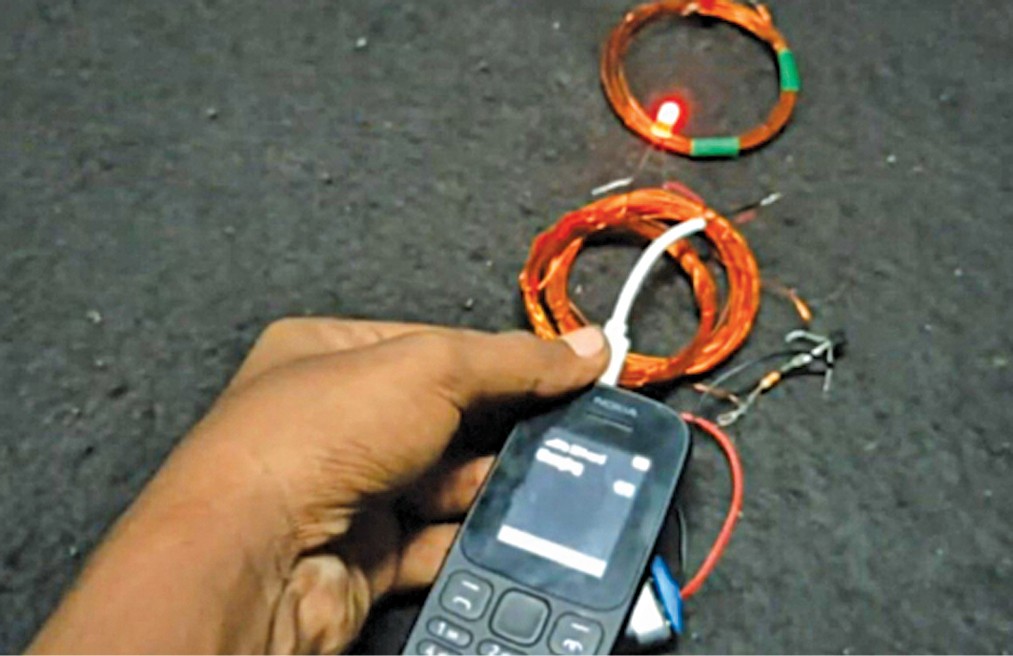
Smartphone batteries have to be charged continuously, usually greater than as soon as a day. However their charging cables are inclined to get broken after a while because of extreme use, which will be annoying—particularly in the event that they fail when these are wanted essentially the most. A wi-fi charger could be a handy different; you merely set it up and overlook it. However how does it work, precisely?
Smartphone batteries have to be charged continuously, usually greater than as soon as a day. However their charging cables are inclined to get broken after a while because of extreme use, which will be annoying—particularly in the event that they fail when these are wanted essentially the most. A wi-fi charger could be a handy different; you merely set it up and overlook it. However how does it work, precisely?

Whereas wi-fi charging might seem to be a current invention, its origin dates to greater than 100 years. The credit score for it goes to the well-known Serbian-American inventor, Nikola Tesla.
Working precept
Within the late 1800s, Nikola Tesla efficiently transmitted electrical energy by means of the air. He used a course of referred to as resonant-inductive coupling for it, which works by making a magnetic discipline between a transmitter (to ship electrical energy) and a receiver (to obtain the electrical energy) to energy gentle bulbs in his New York Metropolis laboratory.

Just a few years later, he patented the Tesla coil—a tower with a coil on the high that shot bolts of electrical energy. Tesla had a lot grander imaginative and prescient of a wi-fi energy grid, however his desires have been by no means realised. Now the identical fundamental precept of inductive charging can be utilized for a smartphone’s charging wirelessly.
| Invoice Of Materials | ||
| Element | Amount | Goal |
| 0.3 – 0.4mm dia enamelled copper wire | 5 metres | For transmitter and receiver coils |
| Resistor 1k | 1 | For present limiting |
| Transistor BC547 | 1 | For switching |
| LED | 1 | For half-wave rectifier |
| USB cable | 1 | For charging cell |
| 9V battery with connector | 1 | For transmitter energy provide |
Development
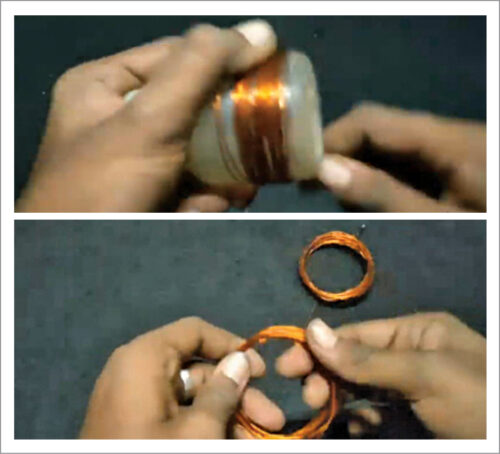
Chances are you’ll use a plastic bottle having about 8cm dia, just like the writer, for winding a coil over it. Or you should use a PVC pipe or another cylindrical object to wind the coil. Wind 15 turns of the enamelled copper wire, terminate, and wind one other 15 turns, like a centre-tapped transformer. Equally, wind 15 turns of the enamelled copper wire to make the receiving coil.
The writer used BC547 NPN transistor for oscillator in his circuit, however as a substitute TTC5200 transistor could also be used for higher outcomes.
Join 1k resistor to the transistor’s base to restrict the present. Join the centre-tapped coil to optimistic terminal of the battery whose destructive terminal ought to be linked to the transistor’s emitter. The opposite two ends of the transmitter coil ought to be linked to transistor’s collector and base terminals, as proven in Fig. 3, by means of the 1k current-limiting resistor.
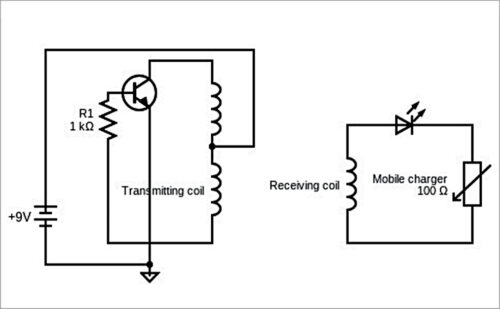
The receiving coil’s ends are linked to the USB cable by means of LED, which is used right here for indication and as a half-wave rectifier.

Precept of operation
The transmitter coil linked to battery by means of the transistor makes the oscillating circuit. The oscillating present contained in the transmitting coil causes it to emit 1MHz magnetic discipline. This oscillating magnetic discipline induces {an electrical} present within the receiver coil.
The induced present is an alternating present, so it must be transformed into DC for cell charging. The LED used within the circuit rectifies the present into DC in addition to its use as an indicator.
Sakthivignesh R. is Engineer – SCADA system