There are millions of totally different switching regulators available on the market. Their election relies on specs reminiscent of enter voltage vary, output voltage functionality, most output present, and another parameters. This text explains present mode, a differentiating characteristic generally listed in knowledge sheets, and its benefits and drawbacks.
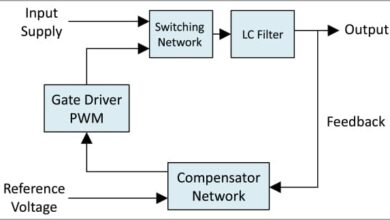
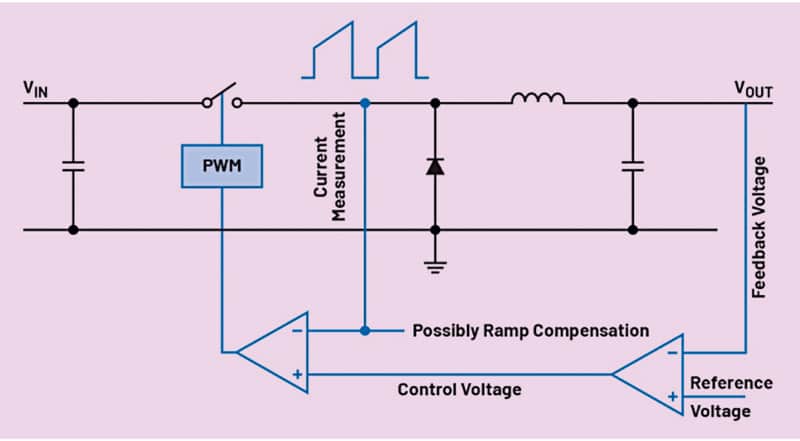
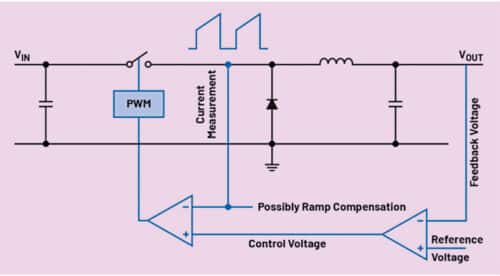
The essential working precept of a current-mode regulator is proven in Fig. 1. Right here, the suggestions voltage isn’t solely simply in contrast with an inside voltage reference but additionally with a sawtooth voltage ramp for the era of the mandatory pulse width modulated (PWM) sign for the ability swap.
The slope of this ramp is mounted in voltage-mode regulators. In current-mode regulators, the slope relies on the inductor present and is yielded from the present measurement proven in Fig. 1 on the switching node. That is what differentiates current-mode regulators from voltage-mode regulators.
Present-mode regulators provide many benefits. One is that the inductor present instantly adapts to modifications within the enter voltage (VIN in Fig. 1). Thus, the enter voltage change info is instantly fed into the management loop, even earlier than the output voltage (VOUT in Fig. 1) tracks this enter voltage change.
Some great benefits of current-mode management are so convincing that almost all switching regulator ICs available on the market work based on this current-mode management precept.
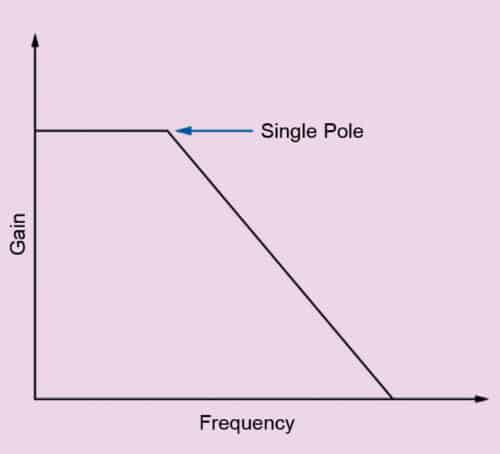
One other key benefit is simplified management loop compensation. The Bode plot of a voltage-mode regulator exhibits a double pole; a current-mode regulator generates only one easy pole of the ability stage at this level. This produces a part shift of 90°, as an alternative of 180° with a double pole. Thus, a current-mode regulator could be rather more simply compensated and thus stabilised. Fig. 2 exhibits the straightforward switch operate of the ability stage of a typical current-mode regulator.
Nevertheless, a couple of disadvantages exist alongside the talked about benefits. Present-mode regulators can not instantly make the required present measurements after a switching transition as a result of the noise will couple into the measurement strongly presently. It takes a couple of nanoseconds for the noise brought on by the switching to subside. That is referred to as the blanking time. It usually ends in a considerably longer mini
mum on-time specification than for voltage-mode regulators.
One other drawback of current-mode regulators is the chance, in precept, of a subharmonic oscillation. That is proven in Fig. 3. If an obligation cycle of better than 50% is required, a current-mode regulator could alternately execute brief and lengthy pulses. In lots of purposes, that is thought of instability, which must be prevented.
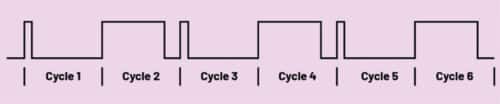
To resolve this, a sure ramp compensation could be added to the generated present ramp proven in Fig. 1. It might probably shift the crucial obligation cycle threshold to properly above 50% in order that even at increased obligation cycles, no subharmonic oscillations happen.
Even these earlier talked about restrictions, as a result of blanking time and the resultant obligation cycle limitations, could be circumvented by way of the IC design. For instance, one treatment is to include low-side present sensing the place the inductor present is measured through the off time quite than the on time.
All in all, the benefits of current-mode management in switching regulators outweigh the disadvantages for many purposes. And thru numerous circuit improvements and modifications, the disadvantages could be bypassed. Because of this, most switching regulator ICs immediately use current-mode management.
Frederik Dostal has greater than 20 years of expertise on this trade. After working in Nationwide Semiconductor since 2001, he joined Analog Units in 2009, the place he held numerous positions, and at present works within the ADI workplace in Munich, Germany as an influence administration skilled